Nearest Neighbor Classification#
Learning from training data#
A key concept in machine learning is using a subset of a dataset to train an algorithm to make estimates on a separate set of test data. The quality of the machine learning and algorithm can be assesed based on the accuracy of the predictions made on test data. Many times there are also parameters sometimes termed hyper-parameters which can be optimized through an iterative approach on test or validation data. In practice a dataset is randomly split into training and test sets using sampling.
k nearest neighbor#
We will examine one machine learning algorithm in the laboratory, k nearest neighbor. Many of the concepts are applicable to the broad range of machine learning algorithms available.
Nearest neighbor concept#
The training examines the characteristics of k nearest neighbors to the data point for which a prediction will be made. Nearness is measured using several different metrics with Euclidean distance being a common one for numerical attributes.
Euclidean distance:
1-D:
2-D:
For multiple points (rows, multidimensional):
import numpy as np
from datascience import *
import matplotlib
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use('ggplot')
Distance function inspired from above equations (1-3).#
def distance(pt1, pt2):
"""The distance between two points, represented as arrays."""
return np.sqrt(np.sum((pt2-pt1)**2))
Nearest neighbor Functions#
These cells create the complete algorithm and use as part of a nearest neighbor toolbox
def row_distance(row1, row2):
"""The distance between two rows of a table."""
return distance(np.array(row1), np.array(row2)) # Need to convert rows into arrays
def distances(training, test, target, features):
"""Compute the distance from test for each row in training."""
dists = []
attributes = training.select(features)
for row in attributes.rows:
dists.append(row_distance(row, test))
return training.with_column('Distance', dists)
def closest(training, test, k, target, features):
"""Return a table of the k closest neighbors to example row from test data."""
return distances(training, test, target, features).sort('Distance').take(np.arange(k))
Prediction Functions#
def predict_knn(row, train, test, k=5, pr=False):
"""Return the predicting value or class among the
k nearest neighbors, pr=1 prints"""
if pr:
print(f'Predicting target value, {target[0]}, for row = {row} using k={k} with features: {features}')
return np.average(closest(train, test.select(features).row(row), k , target, features).column(target[0]))
def predict_knn_class(row, train, test, k=5, pr=False):
"""Return the predicting value or class among the
k nearest neighbors, pr=1 prints"""
closestclass = list(closest(train, test.select(features).row(row), k , target, features).column(target[0]))
if pr:
print(f'Predicting target value, {target[0]}, for row = {row} using k={k} with features: {features}')
print(f'Actual classification: {test.select(target).take(row)[0][0]}')
print(f'Predicted classification: {max(closestclass, key=closestclass.count)}')
print(f'Closest classifications: {closestclass}')
return max(closestclass, key=closestclass.count)
Regression Functions#
Use as part of a toolbox for later analysis and the project
def standard_units(any_array):
"Convert any array of numbers to standard units."
return (any_array - np.mean(any_array))/np.std(any_array)
def correlation(t, label_x, label_y):
"""Compute the correlation between two variables from a Table with column label_x and label_y.."""
return np.mean(standard_units(t.column(label_x))*standard_units(t.column(label_y)))
def slope(t, label_x, label_y):
"""Compute the slope between two variables from a Table with column label_x and label_y."""
r = correlation(t, label_x, label_y)
return r*np.std(t.column(label_y))/np.std(t.column(label_x))
def intercept(t, label_x, label_y):
"""Compute the slope between two variables from a Table with column label_x and label_y."""
return np.mean(t.column(label_y)) - slope(t, label_x, label_y)*np.mean(t.column(label_x))
Classification example#
CKD=Table().read_table('data/ckd.csv')
CKD
| Age | Blood Pressure | Specific Gravity | Albumin | Sugar | Red Blood Cells | Pus Cell | Pus Cell clumps | Bacteria | Blood Glucose Random | Blood Urea | Serum Creatinine | Sodium | Potassium | Hemoglobin | Packed Cell Volume | White Blood Cell Count | Red Blood Cell Count | Hypertension | Diabetes Mellitus | Coronary Artery Disease | Appetite | Pedal Edema | Anemia | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48 | 70 | 1.005 | 4 | 0 | normal | abnormal | present | notpresent | 117 | 56 | 3.8 | 111 | 2.5 | 11.2 | 32 | 6700 | 3.9 | yes | no | no | poor | yes | yes | 1 |
| 53 | 90 | 1.02 | 2 | 0 | abnormal | abnormal | present | notpresent | 70 | 107 | 7.2 | 114 | 3.7 | 9.5 | 29 | 12100 | 3.7 | yes | yes | no | poor | no | yes | 1 |
| 63 | 70 | 1.01 | 3 | 0 | abnormal | abnormal | present | notpresent | 380 | 60 | 2.7 | 131 | 4.2 | 10.8 | 32 | 4500 | 3.8 | yes | yes | no | poor | yes | no | 1 |
| 68 | 80 | 1.01 | 3 | 2 | normal | abnormal | present | present | 157 | 90 | 4.1 | 130 | 6.4 | 5.6 | 16 | 11000 | 2.6 | yes | yes | yes | poor | yes | no | 1 |
| 61 | 80 | 1.015 | 2 | 0 | abnormal | abnormal | notpresent | notpresent | 173 | 148 | 3.9 | 135 | 5.2 | 7.7 | 24 | 9200 | 3.2 | yes | yes | yes | poor | yes | yes | 1 |
| 48 | 80 | 1.025 | 4 | 0 | normal | abnormal | notpresent | notpresent | 95 | 163 | 7.7 | 136 | 3.8 | 9.8 | 32 | 6900 | 3.4 | yes | no | no | good | no | yes | 1 |
| 69 | 70 | 1.01 | 3 | 4 | normal | abnormal | notpresent | notpresent | 264 | 87 | 2.7 | 130 | 4 | 12.5 | 37 | 9600 | 4.1 | yes | yes | yes | good | yes | no | 1 |
| 73 | 70 | 1.005 | 0 | 0 | normal | normal | notpresent | notpresent | 70 | 32 | 0.9 | 125 | 4 | 10 | 29 | 18900 | 3.5 | yes | yes | no | good | yes | no | 1 |
| 73 | 80 | 1.02 | 2 | 0 | abnormal | abnormal | notpresent | notpresent | 253 | 142 | 4.6 | 138 | 5.8 | 10.5 | 33 | 7200 | 4.3 | yes | yes | yes | good | no | no | 1 |
| 46 | 60 | 1.01 | 1 | 0 | normal | normal | notpresent | notpresent | 163 | 92 | 3.3 | 141 | 4 | 9.8 | 28 | 14600 | 3.2 | yes | yes | no | good | no | no | 1 |
... (148 rows omitted)
Define target and features#
target = ['Class']
features = ['Blood Pressure','Blood Glucose Random','Hemoglobin','Serum Creatinine' ]
sCKD = CKD.select(target[0])
Standardize#
for label in features:
print('Standardizing: ',label)
sCKD = sCKD.with_columns(label,standard_units(CKD[label]))
sCKD
Standardizing: Blood Pressure
Standardizing: Blood Glucose Random
Standardizing: Hemoglobin
Standardizing: Serum Creatinine
| Class | Blood Pressure | Blood Glucose Random | Hemoglobin | Serum Creatinine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.363613 | -0.221549 | -0.865744 | 0.52525 |
| 1 | 1.43173 | -0.947597 | -1.45745 | 1.63351 |
| 1 | -0.363613 | 3.84123 | -1.00497 | 0.166693 |
| 1 | 0.534056 | 0.396364 | -2.81488 | 0.623038 |
| 1 | 0.534056 | 0.643529 | -2.08395 | 0.557846 |
| 1 | 0.534056 | -0.561402 | -1.35303 | 1.79649 |
| 1 | -0.363613 | 2.04928 | -0.413266 | 0.166693 |
| 1 | -0.363613 | -0.947597 | -1.28342 | -0.420035 |
| 1 | 0.534056 | 1.87936 | -1.10939 | 0.786018 |
| 1 | -1.26128 | 0.489051 | -1.35303 | 0.36227 |
... (148 rows omitted)
Train, test split#
trainK, testK = sCKD.split(int(0.8*CKD.num_rows))
print(trainK.num_rows, 'training and', testK.num_rows, 'test instances.')
trainK.show(3)
126 training and 32 test instances.
| Class | Blood Pressure | Blood Glucose Random | Hemoglobin | Serum Creatinine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.534056 | -0.576849 | 0.630914 | -0.322247 |
| 0 | 0.534056 | -0.762223 | 0.770138 | -0.517823 |
| 1 | -0.363613 | 2.04928 | -0.413266 | 0.166693 |
... (123 rows omitted)
predict_knn_class(16, trainK, testK, k=8, pr=True)
Predicting target value, Class, for row = 16 using k=8 with features: ['Blood Pressure', 'Blood Glucose Random', 'Hemoglobin', 'Serum Creatinine']
Actual classification: 0
Predicted classification: 0
Closest classifications: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
0
Test prediction accuracy using specified features#
correct = 0
predict_list = []
for i in np.arange(testK.num_rows):
predict = predict_knn_class(i, trainK, testK, k=8, pr=False)
predict_list.append(predict)
correct += 1*(predict == testK[target[0]][i])
print(f'Percent correct: {correct/testK.num_rows*100:.1f}%')
Percent correct: 96.9%
Convert test data to original units and plot using below functions#
Examine relationship between two variables and prediction (0 = no CKD, 1 = CKD)
def original_val(x_z,xmean,xstd):
"""Convert standard z-value back to original"""
x = x_z*xstd + xmean
return x
def plot_relate(tbl, test, predict_list, labelx, labely):
"""Plot prediction in original units"""
testvals = Table().with_columns(target[0],testK[target[0]], 'predict',predict_list)
for label in features:
xmean = np.mean(tbl[label])
xstd = np.std(tbl[label])
x = original_val(test[label],xmean,xstd)
testvals=testvals.with_columns(label,x)
scatter = plt.scatter(testvals[labelx],testvals[labely], c=testvals['predict'])
plt.xlabel(labelx)
plt.ylabel(labely)
plt.legend(*scatter.legend_elements())
return testvals
plot_relate(CKD, testK, predict_list, "Blood Glucose Random", "Hemoglobin")
| Class | predict | Blood Pressure | Blood Glucose Random | Hemoglobin | Serum Creatinine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 70 | 100 | 16.4 | 0.5 |
| 0 | 0 | 60 | 109 | 15.8 | 1.1 |
| 0 | 0 | 70 | 102 | 15 | 1.2 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 122 | 17 | 1.2 |
| 0 | 0 | 70 | 83 | 16.2 | 1.2 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 85 | 15.6 | 1.1 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 132 | 17.8 | 0.8 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 78 | 16.1 | 0.6 |
| 0 | 0 | 70 | 113 | 16.5 | 0.6 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 96 | 13.8 | 0.5 |
... (22 rows omitted)
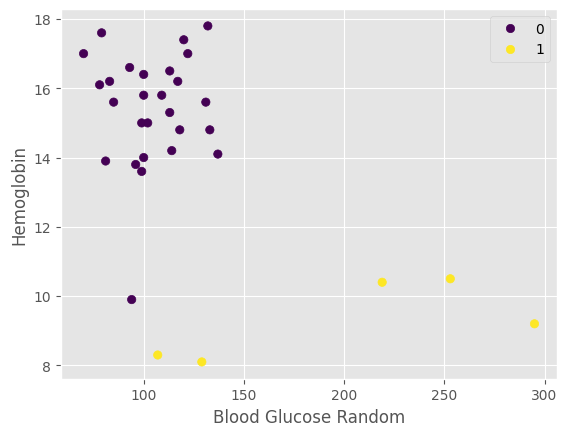
Interpretation: Patients with high hemoglobin numbers and low blood glucose are less likely to be predicted to have CKD
plot_relate(CKD, testK, predict_list, "Blood Glucose Random", "Serum Creatinine")
| Class | predict | Blood Pressure | Blood Glucose Random | Hemoglobin | Serum Creatinine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 70 | 100 | 16.4 | 0.5 |
| 0 | 0 | 60 | 109 | 15.8 | 1.1 |
| 0 | 0 | 70 | 102 | 15 | 1.2 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 122 | 17 | 1.2 |
| 0 | 0 | 70 | 83 | 16.2 | 1.2 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 85 | 15.6 | 1.1 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 132 | 17.8 | 0.8 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 78 | 16.1 | 0.6 |
| 0 | 0 | 70 | 113 | 16.5 | 0.6 |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | 96 | 13.8 | 0.5 |
... (22 rows omitted)
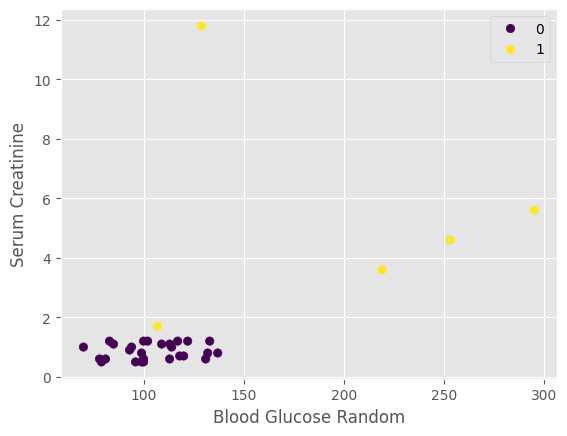
Interpretation: Patients with low creatinine and blood glucose are less likely to be predicted to have CKD
Pretty good prediction, let’s see if we can do better with additional features
Add additional features#
features
['Blood Pressure', 'Blood Glucose Random', 'Hemoglobin', 'Serum Creatinine']
target = ['Class']
features = ['Age','Blood Pressure','Blood Glucose Random','Hemoglobin','Serum Creatinine', 'Sodium', 'Blood Urea' ]
sCKD = CKD.select(target[0])
for label in features:
print('Standardizing: ',label)
sCKD = sCKD.with_columns(label,standard_units(CKD[label]))
sCKD
Standardizing: Age
Standardizing: Blood Pressure
Standardizing: Blood Glucose Random
Standardizing: Hemoglobin
Standardizing: Serum Creatinine
Standardizing: Sodium
Standardizing: Blood Urea
| Class | Age | Blood Pressure | Blood Glucose Random | Hemoglobin | Serum Creatinine | Sodium | Blood Urea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.101098 | -0.363613 | -0.221549 | -0.865744 | 0.52525 | -3.73015 | 0.0724741 |
| 1 | 0.222253 | 1.43173 | -0.947597 | -1.45745 | 1.63351 | -3.32831 | 1.15195 |
| 1 | 0.868954 | -0.363613 | 3.84123 | -1.00497 | 0.166693 | -1.05122 | 0.157139 |
| 1 | 1.19231 | 0.534056 | 0.396364 | -2.81488 | 0.623038 | -1.18517 | 0.792125 |
| 1 | 0.739614 | 0.534056 | 0.643529 | -2.08395 | 0.557846 | -0.515439 | 2.01976 |
| 1 | -0.101098 | 0.534056 | -0.561402 | -1.35303 | 1.79649 | -0.381492 | 2.33726 |
| 1 | 1.25698 | -0.363613 | 2.04928 | -0.413266 | 0.166693 | -1.18517 | 0.728626 |
| 1 | 1.51566 | -0.363613 | -0.947597 | -1.28342 | -0.420035 | -1.8549 | -0.435514 |
| 1 | 1.51566 | 0.534056 | 1.87936 | -1.10939 | 0.786018 | -0.1136 | 1.89277 |
| 1 | -0.230439 | -1.26128 | 0.489051 | -1.35303 | 0.36227 | 0.288239 | 0.834457 |
... (148 rows omitted)
trainK, testK = sCKD.split(int(0.8*CKD.num_rows))
print(trainK.num_rows, 'training and', testK.num_rows, 'test instances.')
trainK.show(3)
126 training and 32 test instances.
| Class | Age | Blood Pressure | Blood Glucose Random | Hemoglobin | Serum Creatinine | Sodium | Blood Urea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -0.424449 | -1.26128 | -0.221549 | -0.239236 | -0.485227 | 0.288239 | -0.160354 |
| 0 | 0.610274 | -1.26128 | -0.283341 | 0.561302 | -0.354843 | 0.0203463 | -0.62601 |
| 0 | 0.351593 | 0.534056 | 0.025616 | -0.169624 | -0.322247 | -0.515439 | -0.753007 |
... (123 rows omitted)
Test prediction accuracy using specified features#
correct = 0
predict_list = []
for i in np.arange(testK.num_rows):
predict = predict_knn_class(i, trainK, testK, k=8, pr=False)
predict_list.append(predict)
correct += 1*(predict == testK[target[0]][i])
print(f'Percent correct: {correct/testK.num_rows*100:.1f}%')
Percent correct: 93.8%
plot_relate(CKD, testK, predict_list, "Blood Urea", "Sodium")
| Class | predict | Age | Blood Pressure | Blood Glucose Random | Hemoglobin | Serum Creatinine | Sodium | Blood Urea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 43 | 80 | 81 | 13.9 | 0.6 | 135 | 46 |
| 0 | 0 | 35 | 60 | 105 | 14.7 | 0.5 | 135 | 39 |
| 1 | 0 | 62 | 70 | 122 | 12.6 | 1.7 | 136 | 42 |
| 0 | 0 | 25 | 80 | 121 | 15 | 1.2 | 142 | 19 |
| 0 | 0 | 43 | 80 | 130 | 15.9 | 1.1 | 143 | 30 |
| 0 | 0 | 55 | 80 | 104 | 17.3 | 0.9 | 142 | 28 |
| 0 | 0 | 58 | 70 | 88 | 16.4 | 1.1 | 147 | 16 |
| 0 | 0 | 20 | 70 | 123 | 14.6 | 1 | 135 | 44 |
| 0 | 0 | 68 | 60 | 125 | 17.4 | 1.1 | 139 | 41 |
| 0 | 0 | 12 | 80 | 100 | 15.8 | 0.6 | 137 | 26 |
... (22 rows omitted)
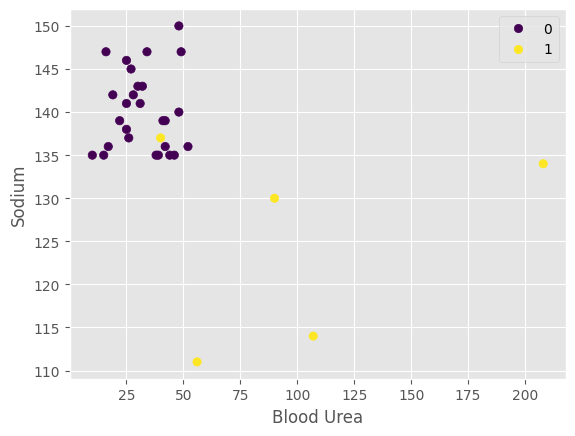
Interpretation: Patients with high sodium and low urea are less likely to be predicted to have CKD
Improved…
